Topics on this page
Inspect inbound traffic with Azure Application Gateway
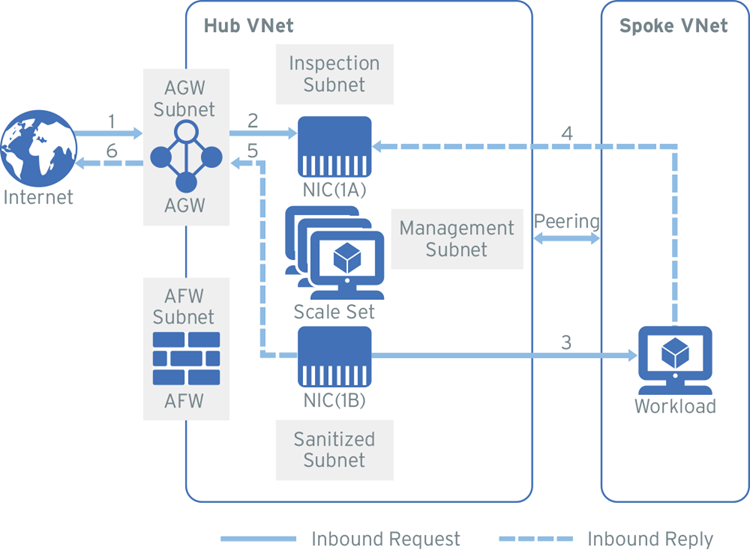
This deployment option describes how to deploy a scale set of virtual appliances with an Azure Application Gateway. The Application Gateway allows you to manage web application traffic. Learn more.
The following diagram shows an example of the traffic flow for this deployment:
IMPORTANT: Internet connectivity notice
During the Deploy the Network Security virtual appliance step, the Network Security virtual appliance is configured behind a standard internal load balancer. The placement of this load balancer blocks the outbound internet connectivity by default unless internet connectivity has been explicitly declared. For this deployment, add a NAT gateway to the management subnet to allow outbound connectivity so that your Network Security virtual appliance can communicate with Network Security. This option is configured before the Network Security virtual appliance is deployed.
Complete these tasks to set up your environment:
- Create a resource group
- Create spoke virtual network and subnets
- Create hub virtual network and subnets
- Add peering to connect the hub and spoke-VNets
- Add a NAT gateway to the management subnet
- Configure the application gateway
- Deploy the Network Security virtual appliance
- Configure route tables and rules
Before you begin
- Review Azure's naming conventions.
- Set up Azure Monitor. Write down the Log Monitor Workspace ID and Log Monitor Primary Key.
- Generate a Trend Micro Cloud One appliance deployment token.
Configure inbound inspection
Create a resource group
Create a resource group if one does not already exist in your environment.
- Navigate to Resource groups → + Add.
- Select your Subscription, name the resource group, then select a region.
- Click Review + Create.
Create the spoke virtual network and two subnets
- Navigate to Virtual Networks → + Add.
- Enter values for the fields in the Basics tab, naming the instance
Spoke-VNet. - In the IP Address tab, edit the IPv4 address space and enter a new address.
- Click + Add Subnet and enter these details:
- Subnet name:
WorkloadSubnet - Address range (example): 10.3.1.x/xx
- Subnet name:
- Click OK.
- Click + Add Subnet and enter these details:
- Subnet name:
AGW-Subnet - Address range (example): 10.3.2.x/xx
- Subnet name:
- Skip the Security and Tags tabs.
- Click Review + Create, and then click Create.
Create a Workload virtual machine (optional)
Follow these steps if you are creating this environment as a proof of concept or if you do not have an existing workload in your environment.
- Navigate to Virtual machines → + Add → Virtual machine.
- In the Basics tab, fill in the required fields. Enter the following for the Name and Inbound port rules:
- Name:
WorkloadVM - Public inbound ports: None
- Name:
- In the Disks tab, select Standard HDD for the OS disk type and configure the other settings.
- In the Networking tab, enter these values:
- Virtual network:
<Your Spoke-VNet> - Subnet:
WorkloadSubnet - Public inbound ports: None
- Virtual network:
- Fill in the information in the remaining tabs.
- Click Review + Create, and then click Create.
- Write down the Private IP address after the deployment is complete.
Backend workloads example
If you followed the steps above to create a workload in your Azure environment, the following table provides an example of configuration details for two virtual machine web workloads. Install an HTTP server if you intend to configure backend workloads after they are created.
| Network interface | Subnet | IP example |
|---|---|---|
| WebWorkloadA | WorkloadSubnet1 | 10.0.x.1 |
| WebWorkloadB | WorkloadSubnet2 | 10.0.x.2 |
Create the hub inspection virtual network and subnets
Use the procedure below to manually set up the inspection-VNet (hub) and subnets. You will select all of the subnets when you deploy your Network Security virtual appliance.
-
Navigate to Virtual Networks → Add.
-
Enter values for the fields in the Basics tab, naming the instance
Hub-VNet. -
In the IP Address tab, edit the IPv4 address space and enter a CIDR.
-
Click + Add Subnet and enter this information to create four subnets:
Subnet name Subnet CIDR examples Management-subnet10.0.0.x/xx Inspection-subnet10.0.1.x/xx Sanitized-subnet10.0.2.x/xx LoadBalancer-subnet10.0.3.x/xx -
Click Review + Create, and then click Create.
Add peering to connect the hub and spoke VNets
- Navigate to the Virtual networks page.
- Click into the Hub-VNet → Peerings → + Add.
- The first peering connection is from the Hub to the Spoke-VNet. Enter the following configuration details, then click Ok.
- Peering connection name:
Spoke-to-Hub - Virtual network deployment model: Resource manager
- Subscription: Your subscription
- Virtual network:
<your Spoke VNet> - Peering connection name:
Hub-to-Spoke - Allow virtual network access from Hub-VNet to Spoke-VNet: Enabled
- Allow virtual network access from Spoke-VNet to Hub_VNet: Enabled
- Allow forwarded traffic from Spoke-to-Hub: Enabled
- Allow virtual network access from Hub-to-Spoke: Enabled
- Allow gateway transit: Leave unchecked
- Peering connection name:
Add a NAT gateway to the management subnet
As described in the Internet connectivity notice section, add a NAT gateway associated with the management subnet to your configuration to allow the Network Security virtual appliance to communicate with Network Security.
NOTE
There is an option to automatically generate a NAT gateway when you deploy the Network Security virtual appliance. Select the option to automatically generate the NAT gateway in the Deploy the Network Security virtual appliance section or use these steps to manually deploy the NAT gateway.
- Navigate to NAT gateways → + Add.
- Enter the required information on the Basics tab.
- In the Outbound IP tab, select Public IP addresses or Public IP prefixes depending on your resources.
- Public IP address: A single IP address
- Public IP prefixes: A range of public IP addresses
- In the Subnet tab, select your Hub-VNet name, then select the management-subnet.
- Click Review + Create, and then click Create.
The management subnet can be associated after the NAT gateway is created by clicking the Subnet menu option from the NAT gateway details page.
Configure the Application Gateway
-
Navigate to Application gateways → + Add.
-
In the Basics tab, enter these values:
- Application Gateway name:
AGW - Region: Select the same region as your resource group
- Minimum scale units: Enter a unit depending on your environment (see note at bottom of steps).
-
Virtual network:
<Your Spoke-VNet> -
Subnet:
AGW-subnet
- Application Gateway name:
-
In the Frontends tab, enter these values:
- Frontend IP address type: Public
- Public IP address: Click Create a new public IP
-
In the Backends tab, click Add a backend pool and enter these values:
- Name:
Webpool - Target type:
Virtual Machine(create two of these) - Target:
web-workload-aandweb-workload-b(create one of each)
- Name:
-
In the Configuration tab, click Add a routing rule and enter these values:
- Rule name:
HTTP_Normal - Listener name:
PORT80_Listener - Frontend IP:
Public - Port:
80
- Rule name:
-
In the same screen, navigate to the Backend targets tab and enter these values:
- Target type: Backend pool
- Backend target:
Webpool - HTTP settings:
HTTP_Normal
-
Click Add.
-
Configure any Tags you want to add.
-
Click Review + Create, and then click Create.
NOTE
AGW is a fully dynamic auto-scaling service that automatically changes the number of its service based on the amount of requested traffic. The minimum scale unit setting is used to guarantee a minimum number of instances running so response time stays relatively stable. Entering a zero means the service will shrink to zero when there is no traffic.
Deploy the Network Security virtual appliance
The Network Security virtual appliance is available from the Azure Marketplace as a public offer. To deploy the Network Security virtual appliance, navigate to Azure Portal → Marketplace → Trend Micro Cloud One™ – Network Security.
Manually add virtual appliances to Trend Micro Cloud One if the Azure Marketplace deployment does not properly register the virtual appliance(s) to Network Security.
Gather the following information before you begin the deployment:
- VNet resource group name.
- Names of the management, inspection (DataportA), sanitized (DataportB), and load balancer subnets.
- Your Trend Micro Cloud One appliance deployment token
- Log Analytics workspace ID and Primary Key - Register your Log Analytics workspace during the deployment process so that your logs will be sent to the Network Security management interface.
Note
Best practice is to copy and paste the exact names of the resource group, hub-VNet, and subnets.
- Log into Azure and select Create a resource (this will direct you to the Marketplace).
- Search for Trend Micro Network Security.
- Next to Select a plan, choose Scale Set VM in the dropdown menu.
- Click Create.
- Enter the following information in the Basics tab:
- Enter your Trend Micro Cloud One appliance deployment token
- If selected, create a public user key (SSH key)
- Select the following information in the Networking tab:
- Your virtual network.
- All of the subnets you created in the inspection-VNet.
- For NAT Gateway, either choose Create new to automatically create a new NAT gateway when you deploy the virtual appliance, or choose Select existing if you already manually created a NAT gateway.
- Enter or select the following information in the Advanced tab:
- (Suggested) Keep the Boot diagnostics setting enabled.
- Select your boot diagnostic account, or create a new one.
- Enter the Log Analytics workspace ID and Primary Key in order to upload your logs to the Network Security management portal.
- Click Review + Create, and then click Deploy.
Configure route tables and rules
After the Network Security virtual appliance is deployed, add and configure the route tables and routes that will place your virtual appliance in-line and begin inspecting traffic. Network traffic is subjected to the firewall rules when network traffic is routed to the firewall as the subnet default gateway.
You will need the following information in order to complete this process:
Locate the frontend IP address of the load balancer
- Navigate to the load balancer.
- Select Frontend IP configuration. The Frontend IP address is in the IP address column.
Step 1: Create two route tables
- Navigate to Route table and click + Add.
- Enter the following values:
- Table one:
AGW-rt - Table two:
Workload-rt
- Table one:
- Leave the Propagate gateway routes setting in its default state. This setting is used to build on-premise-to-cloud environments.
- Click Review + Create, and then click Create.
- Repeat this process for the remaining table.
Step 2: Configure the route tables
Navigate to the Route tables page.
- Select the AGW-rt table, then click Routes → + Add.
- Enter this information:
- Name:
toWorkload - Address prefix:
<CIDR of the Workload-subnet> - Next hop type:
Virtual Appliance - Next hop address:
<Frontend IP address of the LoadBalancer> - Click OK.
- Name:
- Select the Workload-rt table, then click Routes → + Add.
- Name:
toAGW - Address prefix:
<CIDR of the AGW-subnet> - Next hop type:
Virtual Appliance - Next hop address:
<Frontend IP address of the LoadBalancer> - Click OK.
- Name:
Step 3: Associate a route table to its related subnet
- Select your AGW-rt table, then click Subnets → + Associate.
- Virtual network:
Your Spoke-VNet - Subnet:
AGW-subnet
- Virtual network:
- Select your Workload-rt table, then click Subnets → + Associate.
- Virtual network:
Your Spoke-VNet - Subnet:
WorkloadSubnet
- Virtual network:
Configure outbound inspection
Complete these tasks to configure outbound inspection on a scale set of appliances.
Create and configure the AzureFirewall route rules
Create the Firewall
Skip this step if you already have an Azure Firewall or a third party firewall set up.
In the Security tab, select Enable for the Firewall setting and fill in the firewall details.
- Firewall name:
AzureFirewall - Firewall subnet address space (example): 10.0.100.x/x
- Public IP address: Create New → add an IP address.
After you create and deploy the Azure Firewall, make the following configuration changes. Learn more.
Note the Firewall IP information
Private and public IPs are assigned automatically after you create the firewall. Note the IP information for future use in the deployment process.
- Navigate to Firewalls → AzureFirewall.
- Select Public IP Configuration.
- Write down the Private and Public IP addresses for the AzureFirewallSubnet.
Configure the Firewall Network Rule (egress)
- Navigate to All Resources → AzureFirewall.
- Select Rules.
- Click Network rule collection → + Add network rule collection.
-
Enter the following information for Basic information:
- Basic Information
- Name:
NSVA_OUTBOUND - Priority:
100 - Action:
Allow
-
Enter the following information for IP Address Rules:
- Name:
All_outbound - Protocol:
Any - Source Type:
IP Address - Source:
* - Destination Type:
IP Address - Destination Address:
* - Destination Ports:
*
- Name:
- Click Add.
Configure route tables and rules
Network traffic is subjected to the firewall rules when routed to the firewall as the subnet default gateway.
The following information is required to complete this process:
Step 1: Create two additional route tables
- Navigate to Route table and click + Add.
- Enter these values for each route table:
- Table one:
Firewall-rt - Table two:
DataportB-rt
- Table one:
- Click Review + Create, and then click Create.
- Repeat this process for the remaining table.
Step 2: Configure the route tables
Navigate to the Route tables page.
- Select the Workload-rt table, then click Routes → + Add.
- Name:
Default - Address prefix:
0.0.0.0/0 - Next hop type:
Virtual appliance - Next hop address:
<NIC 1A private IP of Network Security virtual appliance> - Click OK.
- Name:
- Select the Firewall-rt table, then click Routes → + Add.
- Name:
Default - Address prefix:
0.0.0.0/0 - Next hop type:
Internet - Click OK.
- Name:
- Add another route to the Firewall-rt table. Click Add.
- Name:
toWorkload - Address prefix:
<CIDR of the Workload subnet> - Next hop type:
Virtual Appliance - Next hop address:
<Frontend IP address of the LoadBalancer> - Click OK.
- Name:
- Select the DataportB-rt table, then click Routes → + Add.
- Name:
Default - Address prefix:
0.0.0.0/0 - Next hop type:
Virtual Appliance - Next hop address:
<Private IP of AzureFirewall> - Click OK.
- Name:
Step 3: Associate a route table to its related subnet
-
Select your Firewall-rt table, then click Subnets → + Associate.
- ** Virtual network:**
Your Hub-VNet - Subnet:
AzureFirewallSubnet
- ** Virtual network:**
-
Select your DataportB-rt table, then click Subnets → + Associate.
- Virtual network:
Your Hub-VNet - Subnet:
Sanitized-subnet
- Virtual network:
Restore traffic using routes
Reference the Configure route tables and rules section. Remove the following user-defined routes for inbound inspection if a virtual appliance experiences an outage.
- Remove
AGW-rtroute table from its associated subnet. - Remove
Workload-rtroute table from its associated subnet.
Manual Fallback
Manually place your virtual appliance(s) in fallback mode by enabling this setting.